Scalping stocks is a fast-paced trading strategy used to obtain profits. The rapid execution of short term trades gives smaller wins per trade, but can accumulate over time into profitable returns. In this tutorial, we review the definition of scalping, popular scalping strategies and specifically what scalping means in stocks trading.
Scalping Stocks Explained
Scalping stocks aims to generate profit from short term share volatility, with a high number of trades at a lower profit per trade. This is executed by rapidly selling after a trade has become profitable and repeating a high number of times. The thinking behind this is that the risk per trade is limited.
This differs from swing trading or position trading strategies where a position would likely be held for longer, with the intention of making a higher profit from a single trade. Although higher returns are possible with longer positions, it’s expected that an increased number of trades would result in some losses too.

Stock scalpers tend to aim for a 1:1 risk-reward ratio on every trade to enable a high number of wins.
High liquidity stock markets are essential to enable the trader to enter and exit trades very quickly. Accurate execution can provide decent returns and some traders even scalp stocks for a living. However, the trading environment is extremely fast-paced and scalping carries a high level of risk if not carried out with precision.
Here, we discuss scalping pros and cons in the context of stocks, though it is also possible to scalp other instruments such as cryptos and forex.
Scalping Stocks Strategies
Scalping can be carried out based on fundamental analysis, which attempts to analyse the stock value by reviewing external events, for example economic news. However, scalping is usually performed using technical analysis, which uses indicators to detect patterns and forecast stock values.
Predicting trends allows traders to make an informed decision about whether the risk-reward ratio is appropriate for scalping. The information extracted about the stock depends on the indicator used.
The internet offers resources for a huge selection of scalping stocks strategies, including YouTube videos where people often carry out scalping trading live. However, this can be overwhelming and you may be left wondering which is the best scalping stock trading strategy.
Simple Moving Average (SMA)
The moving average is a simple method used by scalpers to indicate the trend of stocks by removing noise from the chart.
By constantly updating the average over a selected period of time, the indicator smooths out prices that would otherwise show short term fluctuations. Longer moving average periods result in lower price fluctuations that are more suited to detect long term trends.
SMA Example
Select a 200 day period moving average to indicate the overall trend. Then, select a short term moving average and a slightly longer-term moving average, such as 5 day and 20 day periods, which will indicate whether to buy or sell. A short 1 minute or 5 minute timeframe is the best for this scalping stocks strategy.
- If the 5 day moving average crosses the 20 day moving average, then take the position in the direction of the trend (i.e. as indicated by the 200 day moving average)
- If the moving averages cross each other back, sell
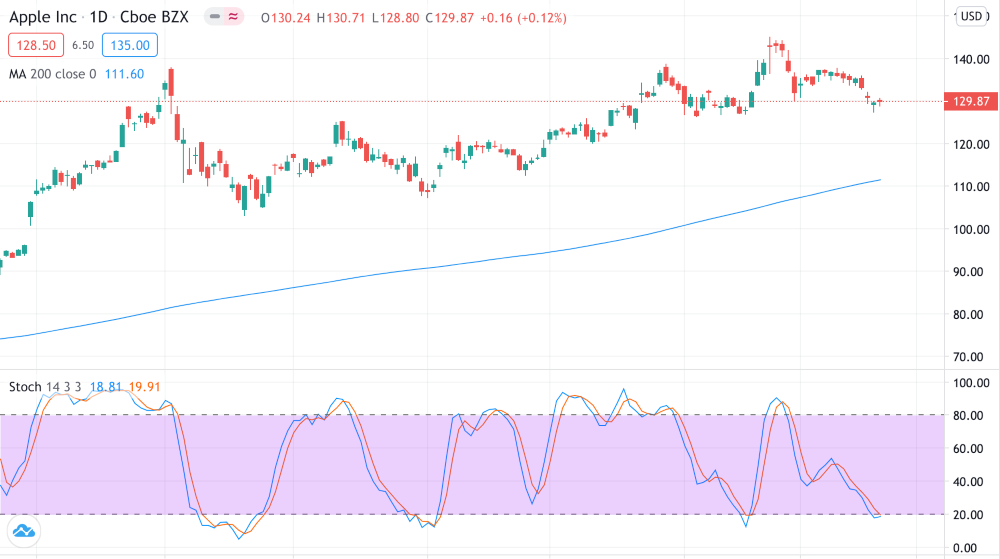
Stochastic Indicator
The stochastic indicator is an indicator of momentum that can also be applied to scalping stocks. It is a value between 0 and 100 that indicates whether a market is oversold (trading below its true value) or overbought (trading above its true value), based on data from previous investing sessions.
Generally, a value over 80 is considered to be overbought, and a value under 20 is considered to be oversold. This is thought to indicate a turning point in the market.
A slow stochastic indicator can be calculated by creating a 3 day moving average of the ‘fast’ indicator. The intersection of these fast and slow oscillators is often considered to be an indication of a reversal.
Stochastic indicators can also be used in combination with the long term moving average as a stock scalping strategy.
- Low stochastic indicators that are trending upwards provide entry points for long positions, while high stochastic indicators that are trending downwards provide entry points for short positions. This method can be used in combination with the moving average indicator, by only trading when the stochastic indicator is in the same direction as the trend according to the SMA. This reduces the likelihood of the stochastic indicator generating a false signal by itself.
- If the stochastic indicator trend continues into the oversold or overbought areas, sell.
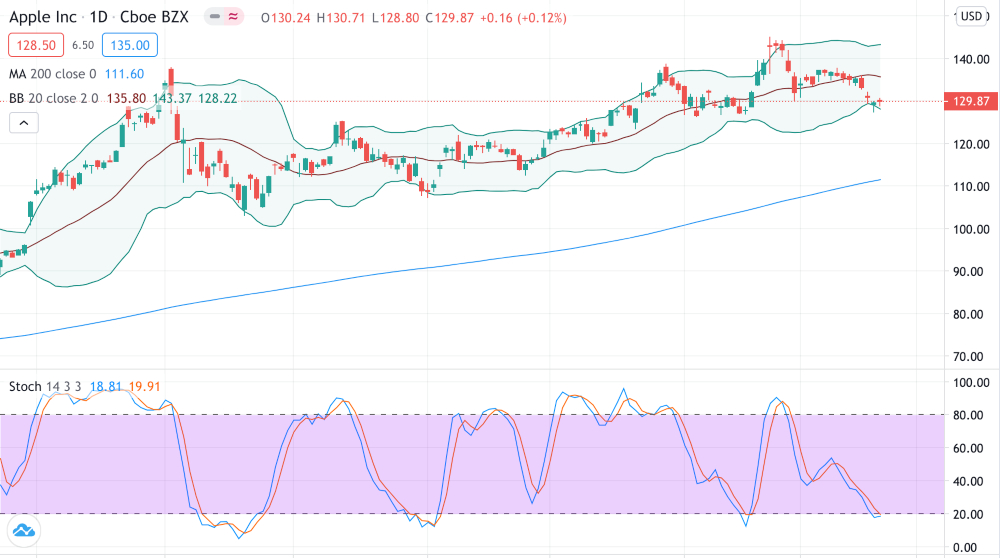
Bollinger Bands
Bollinger Bands can be used to further confirm entry and exit points when scalping stocks, by also determining if a market is overbought or oversold.
They are a set of lines typically plotted two standard deviations away from the simple moving average.
Using Bollinger Bands in combination with the long term moving average and stochastic indicator will add further depth to your analysis:
- When the price hits the lower Bollinger Band and the stochastic indicator is showing the stock is oversold, enter a long position
- When the price hits the upper Bollinger Band and the stochastic indicator is showing the stock is overbought, enter a short position
- If the price touches the top Bollinger Band, sell
In addition, market profile can be used to display further information about market volume and price information, if the stock scalper requires.
How To Start Scalping Stocks
Scalping Brokers
To start scalping stocks you’ll need good stocks scalping brokers which provide you with the required tools. Not all brokers allow scalping, and sometimes it is simply not possible to handle the volume or speed of trades with the platform they offer. Review this list to ensure your broker has everything you require to start scalping stocks:
- Platform – Brokers may offer proprietary platforms or license a platform such as MetaTrader 4.
It is essential that STP or ECN trading is supported by the platform, otherwise the software will not be able to execute trades quickly enough for scalping stocks.
Narrow spreads – Scalping aims to profit off changes in the bid-ask spread. Wide spreads will reduce the likelihood of a profitable trade, so check the difference between trading desks.
Regulation – Check if and where your broker is regulated, as not all regulators offer the same level of financial protection. A good regulator will ensure that your funds are protected if your broker becomes insolvent.
Demo account – Demo accounts are an excellent way to practice trading strategies in real-time, which is particularly important when scalping stocks, as any delays can diminish profits. Check if the broker offers a demo account that is representative of the live account environment.
Automated trading – Stocks scalping is best done using algorithmic bots. On some platforms these will be available to download, for example Expert Advisor (EA) robots on MetaTrader. Some platforms also offer the option for traders to develop bespoke scalping robots using proprietary languages, or more popular programming languages such as Python.
Commission – Beware of high commissions that can be charged for stocks trading, which will quickly eradicate any profits when scalping. Traders should also look out for other broker fees such as account or withdrawal fees.
Leverage – Leverage is almost always necessary when scalping stocks, to increase a position such that it has the potential to return substantial profits.
In particular, pay attention to leverage limits applied to stocks which are usually significantly lower than for other instruments such as forex.
As always, be aware that using leverage can result in larger losses as well as returns.
- Level II quote system – The Level II order book provides more information than Level I trading data, including details of all orders placed.
- Level II quotes therefore allow the stock scalper to better predict the short term direction of the market, when large bids are placed by other traders.
- Check which brokers offer this functionality.
eToro, Plus500 and Trade212 are among the brokers that do not permit scalping of stocks.
Although Robinhood does not charge a commission, it is not well suited to scalping because of the inability to access Level II quote information.
In the UK, IG is a recommended scalping broker, while traders in Canada should look at IC Markets which allows scalping and accepts Canadian clients.
For American traders, TD Ameritrade offers the Thinkorswim desktop platform which is popular with scalpers.
Scalping 101
Here are some basic rules to consider before you start scalping stocks.
Timing
The busiest trading times are best for scalping trading as illiquid markets can lead to higher spreads.
Specifically, 1 – 5 pm GMT is often considered the best time to trade as it is the overlap between the New York and London Stock exchange.
Concentration
Ensure you have a clear plan for scalping that involves focusing on one stock at a time.
This will ensure you don’t get distracted and hold a losing position for too long.
Liquidity
Good scalping stocks are those with high liquidity and volume and are therefore easier to buy and sell. Because of this, scalping is not suitable for penny stocks which have low volume. Recommended indices for stocks scalping are Dow Jones and DAX 40 which have relatively high index values, high liquidity and low spreads. It is also possible to scalp a variety of other stocks and indices including Indian stocks on the NIFTY and ASX200 stocks.
Stops
Stops are vital to prevent large losses in scalping stocks that could counteract any wins. Set your trading stop so that it reflects your risk to reward ratio target. For example, if you are scalping for 6 points with a risk-reward ratio of 2:1, your stop-loss should be set to 3 points.
Risk Management
In addition to stops, there are also other ways to manage risk when scalping stocks. For example, Gamma, one of the ‘Greeks’ parameters used to assess the risk exposure of an asset, can be applied to options scalping to help forecast price moves in the underlying stock.
Research
Scalping stocks is a high-pressure trading environment so ensuring you are confident with your strategy and execution is key. eBooks, online PDFs and forums can be a great way to pick up information about strategies and the best stocks for scalping. Free online courses are also a good way to practice scalping stocks.
Pros Of Scalping Stocks
There are several pros of applying scalping strategies to stocks:
- Quick wins – Traders will see returns quickly, due to the short timescales associated with scalping stocks.
- Flexibility in timing – Scalping can be profitable on markets that do not see overall growth or decline in a day.
- This means that traders don’t need to wait for a strong trend to start scalping stocks.
- Volatility – Stocks have lower volatility than other instruments such as forex, meaning scalping can feel less pressured.
Cons Of Scalping Stocks
Equally, there are many disadvantages of scalping stocks, especially compared with other instruments:
- Potential losses – Scalping stocks uses high leverage which comes with increased risk.This can result in large losses should a losing position remain open longer than necessary.
- High commitment – Scalping stocks can be stressful due to its fast pace.Traders need to keep a level head for a sustained period to generate a profit.
- Emotional impact – It can be emotionally difficult to sell when making a profit, but being disciplined with selling when planned is essential to successfully scalp stocks.And remember, stock scalping is not a game – losses can accumulate quickly.
- Cost – Stock trade volume is lower than instruments such as forex, which generally results in lower liquidity and higher spreads.Additionally, brokers tend to charge a commission for trading stocks, unlike forex.
- Timing – Trading hours depend on the local stock exchange, unlike forex which can be traded 24/5.
- Leverage – The leverage available for stocks is generally lower than other instruments, meaning it can be more difficult to be profitable in stocks scalping vs forex.
However, scalping futures and CFDs can provide greater exposure to the markets vs stocks, which is useful for traders without large capital.
The Difference Between Scalping & Day Trading Stocks
Scalping stock strategies differ to intraday trading with regards to timescales, volume and leverage used. Scalping holds positions for shorter timescales; typically seconds or minutes rather than the hours that might be expected in day trading. In the case of micro-scalping, timescales can be as short as 10-20 seconds. Usually volumes are higher than in day trading and increased leverage is used, to enable the trader to make a profit in shorter periods.
Final Word On Scalping Stocks
Scalping stocks is a deservedly popular trading strategy that opens up opportunities even when the market is trading sideways. However, the pressured environment and potential losses that can be incurred by mistakes mean beginners should be cautious.
FAQ
What does scalping mean in stocks trading?
Scalping is a trading strategy designed to profit from small price changes that can be applied to stocks in the same way as other instruments.
The main consideration is how suitable scalping is for each market. The higher commission fees associated with stocks means it can be more difficult to make a profit by scalping.
Is scalping stocks illegal?
Scalping stocks is legal, however many brokers don’t permit it on their platform. This is often because they do not offer a no dealing desk model and are therefore not able to execute trades quickly enough.
Is scalping stocks trading profitable?
Scalping stocks can be profitable if traders set suitable risk-reward ratios and are disciplined in the execution of their trades. Holding positions for too long increases risk and can result in losses that may wipe out any profits.
Is scalping stocks the same as day trading?
Scalping stocks is not the same as day trading, with timescales of minutes or even seconds rather than hours that would be expected in day trading.
