Position trading is a popular strategy among forex traders for its low maintenance benefits. Nonetheless, position trading is not suitable for everyone and can involve risk. Before you open an account and start investing, see our position trading definition below along with a detailed guide on implementing your own system. We also explore the position trading vs swing or day trading comparison to help you decide which strategy is right for you.
What Is Position Trading?
Position trading aims to generate profits by holding an investment for the longer term, in the hope that the value of the asset will appreciate. As such, the position trader will generally focus less on short-term price movements and daily fundamentals (which would normally be attributed to day trading).
Position trading is often associated with some other forms of financial market trading. If we look at position trading vs trend following, for example, both options actually refer to the same thing. Position traders are trend followers, meaning that once a trend starts, traders believe it is likely to continue in the long term. This also explains why position trading vs momentum trading are often used together.

Position trading vs buy-and-hold investing are also both similar, though the main difference is that the latter involves holding a trading move for even longer than in the former.
This is usually with the aim of working towards a long-term objective, such as retirement.
Position trading is popular for all asset classes, including forex, stocks, commodities, futures and even cryptocurrency such as Bitcoin. Position traders also typically use a mix of technical and fundamental analysis in their strategy.
We’ll cover the basics of some technical strategies later on, along with a detailed explanation on how to start position trading. First, let’s look at the key pros and cons of position trading.
Benefits Of Position Trading
Position trading can come with several benefits, particularly for beginners looking to take their first step in the forex market or those who don’t have much time to dedicate to trading.
- Profit potential – Traders tend to hold larger positions for a longer period of time, which means there can be a greater potential for profit if the trend moves in your favour.
- Comparatively less risk – If you take position trading vs swing, scalping or day trading, there is generally less risk involved with the former. This is because you are placing fewer trades.
- Low maintenance & stress – Position trading is typically defined as a low maintenance and low-stress strategy compared to other forms of trading.
- This means that many traders can easily have a full-time job alongside trading.
- Capitalise on substantial trends – Position traders have the opportunity to capitalise on large and long-term market trends.
Drawbacks Of Position Trading
Regardless of experience level or what you’re trading, there are some drawbacks that may score position trading lower than other strategies.
- Low win rate – Position trading involves placing fewer trades, which in effect means that that the win rate is generally much lower than other types of trading.
- Risk of trend reversals – After a considerable period of stability, the possibility of a trend reversal increases. Whether you’re following forex or commodities, these trading opportunities can often be missed.
- Best for bull markets – Position trading only really suits bull rather than bear markets, whilst sideways trends are usually better for day trading. This potentially limits what assets can be traded consistently with this strategy.
Position Trading Strategies
There are several setups you can use when position trading on weekly, monthly or yearly charts. Note that the below examples won’t suit everyone and you may need to explore other tools when building your position trading strategy, such as moving averages. It’s also important to complement any system with appropriate fundamental analysis and market knowledge.
Support & Resistance Strategy
As one of the most popular position trading strategies, the support and resistance method helps traders to identify which direction an asset is likely to move.
Traders will then either go long when prices increase or short when prices decline.
The support level represents the price that an asset usually does not drop below, as buyers are purchasing at this level. Conversely, the resistance level represents the point buyers stop purchasing and the price, therefore, stops rising.
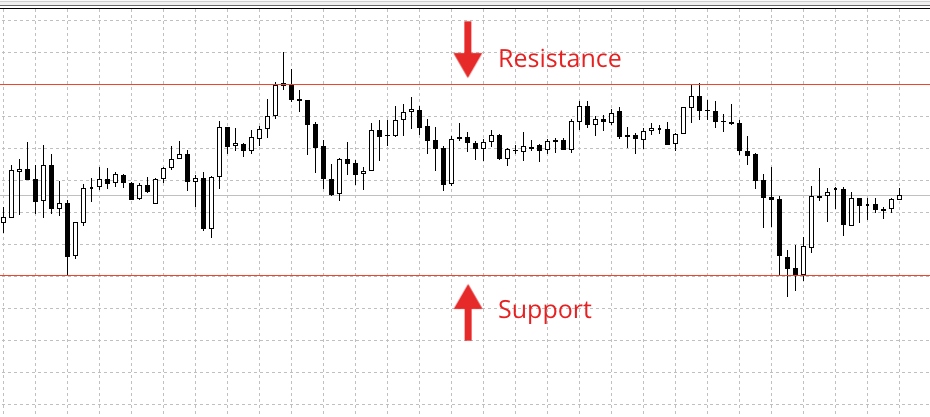
Nonetheless, if the price breaks above resistance, this suggests a period of higher highs and vice versa if it breaks below support. S&R levels are therefore essential for analysing long-term patterns, when taking into consideration historical prices, previous levels of S&R and technical indicators.
Breakout Strategy
As mentioned above, support and resistance levels can be used to identify breakouts in a trend. If the price breaks above resistance or below support, this usually indicates a new trend, where traders will open a long position for the former and a short position for the latter.
Breakouts are an important trading strategy because they are a good example of likely increased volatility. We can then take advantage of this volatility by joining the new trend as it begins. Some traders may use two trend lines acting as support and resistance, which can form triangle shapes or wedges.
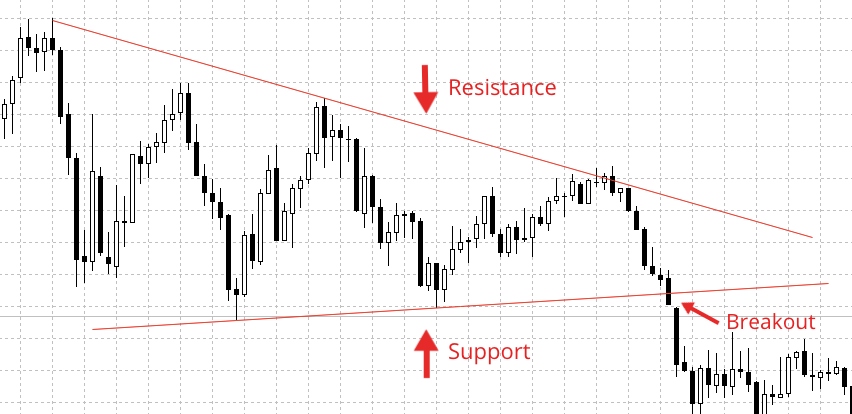
If the market works its way into a wedge pattern, then traders should expect that the trend will break.
If the wedge support is broken, it then becomes the new resistance. This can create the ideal opportunity to enter a short position. Make sure to place your stop loss above or below the breakout candle, at a minimum.
Pullback & Retracement Strategy
A pullback (or retracement) occurs when there is a temporary drop or reversal in an upward trend. Traders can capitalise on these small movements, by buying low and selling high as soon as the asset price moves out of the pullback and continues on the upward trend again.
To avoid confusion with a reversal, which is a long-term or permanent deviation of the trend, you can implement a Fibonacci retracement. The Fibonacci tool will help you determine when to open or close a position.
As you can see below, trading using Fibonacci retracements is represented by six lines on the price chart, initially at 100%, 50% and 0%. Three additional lines will then be drawn at 61.8%, 38.2% and 23.6%, which create the ‘golden ratio’ at which you can identify S & R levels.
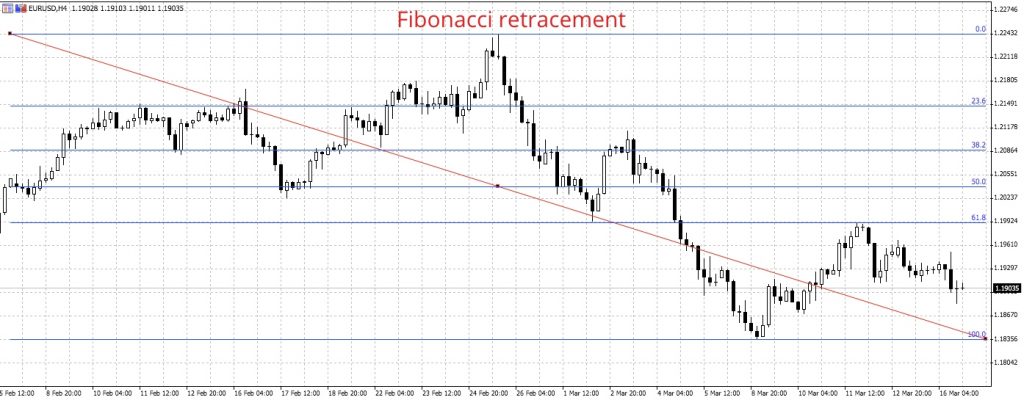
Typically, if the market drops back to 38.2% of the previous rise, traders will see if any buyers come in. If the level gets broken, then it is expected that the 50% line will be the next target.
Market Retracement in Trading
When the market reaches the 50% mark, traders will analyze if it stops declining at the 61.8% retracement level of the previous move. If the price breaks through the 61.8% level, then the market is moving back to where it started.
Starting Position Trading
After familiarizing yourself with popular trading methods, it’s time to find a good broker and implement your own strategy. Consider your priorities and requirements before following our guide on how to start position trading.
1. Finding a Broker
Choose a broker that offers the platforms and fees that suit you. Don’t forget to consider deposit and withdrawal fees, as well as trading commissions. Ensure that the broker is regulated and provides negative balance protection, like AvaTrade, which is regulated in multiple jurisdictions.
Look for brokers with educational resources, training tools, course books, and tutorials. For beginners, eToro is an excellent choice with its user-friendly platform and vast selection of educational materials.
Join trader forums for advice on features like account reports and closing a short position. Trading 212 offers an excellent community forum.
2. Implement Your Strategy
Start position trading by analyzing the market and placing trades based on your chosen strategy. Monitor your positions regularly and adjust as needed.
Choose A Market
Once you’ve chosen your broker, it’s recommended that you take advantage of any demo accounts on offer. This will allow you to browse the trading platforms and practice your strategies without risking your money.

You can also use it to determine which markets you’d like to start position trading. Beginners might opt for popular liquid markets, such as major forex pairs, though you can position trade a wide range of assets on most platforms.
3.Fund Your Account
To start trading, you’ll need to fund your account using one of the payment methods offered by your investing company. Note that there may be a minimum initial payment required, though this is fairly reasonable at most regulated brokers.
Today, brokers typically offer a good selection of payment methods, including bank wire, credit card, or e-wallets such as Skrill or Neteller. Note that these tend to vary depending on your jurisdiction and/or account currency.
4.Implement Your Strategy
You can now start implementing your position trading strategy straight away. Most forex platforms should offer a range of technical analysis tools and fundamental resources via desktop and mobile apps. The MetaTrader platforms, for example, offer an advanced suite of technical indicators and graphical objects, plus multiple timeframes and chart types.
For traders who prefer algorithm-based strategies, it’s also worth looking out for trading bots or automated signals.
An economic calendar is also a useful tool for most trading strategies, as it allows you to keep on top of major news events that could affect the price of the asset.
Other resources might also be helpful for expanding your knowledge of core position trading strategies. This could include strategy management books, such as Trading For Dummies, or online books available via PDF. Some third-party sources can also be helpful, including YouTube and TradingView or expert trader blogs such as Rayner Teo.
5.Use Risk Management
It’s vital that you always implement risk management rules and position size calculators, whatever long or short strategy you use. Any trading strategy can be vulnerable to unpredictable market swings, so always work out your risk profile before opening a trade.
Position sizing refers to the number of trading units you can invest in a security and is determined using a calculator or formula. Some brokers will provide these options within your trading account.
Final Word On Position Trading
Position trading can be fairly straight-forward, though mastering the strategy will require some thorough knowledge of the markets and sound technical analysis skills. If you decide to start position trading, bear in mind the pros and cons and use our guide above as a starting point. Always apply risk management rules to your short and long trades and don’t forget to practice in a demo trading account before depositing your cash.
FAQ
What Is Position Trading?
The definition of position trading is when traders hold an investment for a long period of time with the expectation that the asset will rise in value.
Position traders will focus on long-term price moves by analysing trends and fundamental events.
What Is A Position Trading Firm?
A position trading firm, or broker, is a company that provides a range of financial instruments that can be traded using a trading platform.The firm will charge a fee in the form of a spread markup or commission on each trade.
Is Position Trading Legal?
Yes, position trading is a legal form of trading.However, always ensure you are trading with a safe and regulated broker, in order to keep your funds secure.You may need to check with your local jurisdiction for any restrictions on trading.
Is Position Trading Profitable?
Position trading can generate good returns if using an effective and reliable strategy.
